Heart disease
| Heart disease | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
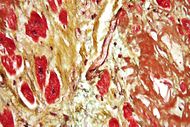 Micrograph a heart with fibrosis (yellow) and amyloidosis (brown). Movat's stain. |
|
| ICD-10 | I00-I52 |
| ICD-9 | 390-429 |
| MeSH | D006331 |
Heart disease or cardiopathy is an umbrella term for a variety of different diseases affecting the heart. As of 2007, it is the leading cause of death in the United States,[1][2] England, Canada and Wales,[3] accounting for 25.4% of the total deaths in the United States.[4]
Contents |
Types
Coronary heart disease
Coronary heart disease refers to the failure of the coronary circulation to supply adequate circulation to cardiac muscle and surrounding tissue. Coronary heart disease is most commonly equated with Coronary artery disease although coronary heart disease can be due to other causes, such as coronary vasospasm.[5]
Coronary artery disease is a disease of the artery caused by the accumulation of atheromatous plaques within the walls of the arteries that supply the myocardium. Angina pectoris (chest pain) and myocardial infarction (heart attack) are symptoms of and conditions caused by coronary heart disease.
Over 459,000 Americans die of coronary heart disease every year.[6] In the United Kingdom, 101,000 deaths annually are due to coronary heart disease.[7]
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy literally means "heart muscle disease" (Myo= muscle, pathy= disease) It is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium (i.e., the actual heart muscle) for any reason. People with cardiomyopathy are often at risk of arrhythmia and/or sudden cardiac death.
- Extrinsic cardiomyopathies – cardiomyopathies where the primary pathology is outside the myocardium itself. Most cardiomyopathies are extrinsic, because by far the most common cause of a cardiomyopathy is ischemia. The World Health Organization calls these specific cardiomyopathies:
- Alcoholic cardiomyopathy
- Coronary artery disease
- Congenital heart disease
- Nutritional diseases affecting the heart
- Ischemic (or ischaemic) cardiomyopathy
- Hypertensive cardiomyopathy
- Valvular cardiomyopathy – see also Valvular heart disease below
- Inflammatory cardiomyopathy – see also Inflammatory heart disease below
- Cardiomyopathy secondary to a systemic metabolic disease
- Myocardiodystrophy
- Intrinsic cardiomyopathies – weakness in the muscle of the heart that is not due to an identifiable external cause.
- Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) – most common form, and one of the leading indications for heart transplantation. In DCM the heart (especially the left ventricle) is enlarged and the pumping function is diminished.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM or HOCM) – genetic disorder caused by various mutations in genes encoding sarcomeric proteins. In HCM the heart muscle is thickened, which can obstruct blood flow and prevent the heart from functioning properly.
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) – arises from an electrical disturbance of the heart in which heart muscle is replaced by fibrous scar tissue. The right ventricle is generally most affected.
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) – least common cardiomyopathy. The walls of the ventricles are stiff, but may not be thickened, and resist the normal filling of the heart with blood.
- Noncompaction Cardiomyopathy – the left ventricle wall has failed to properly grow from birth and such has a spongy appearance when viewed during an echocardiogram.
Cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease is any of a number of specific diseases that affect the heart itself and/or the blood vessel system, especially the veins and arteries leading to and from the heart. Research on disease dimorphism suggests that women who suffer with cardiovascular disease usually suffer from forms that affect the blood vessels while men usually suffer from forms that affect the heart muscle itself. Known or associated causes of cardiovascular disease include diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperhomocysteinemia and hypercholesterolemia.
Types of cardiovascular disease include:
Ischaemic heart disease
- Ischaemic heart disease – another disease of the heart itself, characterized by reduced blood supply to the organs.
Heart failure
Heart failure, also called congestive heart failure (or CHF), and congestive cardiac failure (CCF), is a condition that can result from any structural or functional cardiac disorder that impairs the ability of the heart to fill with or pump a sufficient amount of blood throughout the body. Therefore leading to the heart and body's failure.
- Cor pulmonale, a failure of the right side of the heart.
Hypertensive heart disease
Hypertensive heart disease is heart disease caused by high blood pressure, especially localised high blood pressure. Conditions that can be caused by hypertensive heart disease include:
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Coronary heart disease
- (Congestive) heart failure
- Hypertensive cardiomyopathy
- Cardiac arrhythmias
Inflammatory heart disease

Inflammatory heart disease involves inflammation of the heart muscle and/or the tissue surrounding it.
- Endocarditis – inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. The most common structures involved are the heart valves.
- Inflammatory cardiomegaly
- Myocarditis – inflammation of the myocardium, the muscular part of the heart.
Valvular heart disease
Valvular heart disease is disease process that affects one or more valves of the heart. There are four major heart valve which may be affected by valvular heart disease, including the tricuspid and aortic valves in the right side of the heart, as well as the mitral and aortic valves in the left side of the heart.
See also
- Aneurysm
- Aortic aneurysm
- British Heart Foundation
- Cardiac psychology
- Diet and heart disease
- Endothelium-derived relaxing factor
- High blood pressure (Hypertension)
- National Wear Red Day
- Oral hygiene
- Pericarditis
- Thrombosis
References
- ↑ Division of Vital Statistics; Arialdi M. Miniño, M.P.H., Melonie P. Heron, Ph.D., Sherry L. Murphy, B.S., Kenneth D. Kochanek, M.A. (2007-08-21). "Deaths: Final data for 2004" (PDF). National Vital Statistics Reports (United States: Center for Disease Control) 55 (19): 7. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr55/nvsr55_19.pdf. Retrieved 2007-12-30.
- ↑ White House News. "American Heart Month, 2007". http://georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov/news/releases/2007/02/20070201-2.html. Retrieved 2007-07-16.
- ↑ National Statistics Press Release 25 May 2006
- ↑ National Vital Statistics Reports Volume 58, Number 19. National Center for Health Statistics. 2010-05-01. http://www.cdc.gov/NCHS/data/nvsr/nvsr58/nvsr58_19.pdf. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ Williams MJ, Restieaux NJ, Low CJ (February 1998). "Myocardial infarction in young people with normal coronary arteries". Heart 79 (2): 191–4. PMID 9538315. PMC 1728590. http://heart.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=9538315.
- ↑ American Heart Association: Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2008 Update. AHA, Dallas, Texas, 2008
- ↑ British Heart Statistics report
- ↑ "WHO Disease and injury country estimates". World Health Organization. 2009. http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/estimates_country/en/index.html. Retrieved Nov. 11, 2009.
External links
- VIDEO - Heart Disease in the Female Population: Prevalence, Presentation and Pathophysiology, Mary Zasadil, MD, speaks at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health (2007)
- Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada – Information Resource on Heart Disease
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||